In this guide, let's learn in point about Push Pull Amplifiers. We've covered theory and applications tail a push pull amplifier. We've besides demonstrated different types of push pull amplifiers, suchlike Separate A, Class B and Class Ab push pull amplifier models.
A pushing pull amplifier is an amplifier which has an output stage that backside drive a current in either direction through finished the load. The output stage of a typical force out pull amplifier consists of of two identical BJTs or MOSFETs one sourcing current through the load patc the other one sinking the current from the charge. Push pull amplifiers are superior over single over amplifiers (using a single transistor at the turnout for dynamical the load) in terms of distortion and performance. A only ended amplifier, how well it may be fashioned will for sure introduce many overrefinement ascribable the not linearity of its dynamic transfer characteristics. Push pull amplifiers are usually used in situations where low overrefinement, high efficiency and high end product office are required. The elemental operation of a push pull amplifier is as follows: The signal to be amplified is first split into two identical signals 180° KO'd of form. Generally this splitting is done using an stimulant coupling transformer. The stimulus coupling transformer is so placed that one sign in applied to the input of one transistor and the other signaling is practical to the input of the other junction transistor. Advantages of pushing pluck amplifier are low distortion, absence of magnetic saturation in the sexual union transformer core, and cancellation of power cater ripples which results in the petit mal epilepsy of hum spell the disadvantages are the need of ii identical transistors and the requisite of bulky and costly coupler transformers.
Class A push pull up amplifier.

A push pull amplifier posterior be successful in Class A, Class B, Grade AB or Class C configurations. The circuit diagram of a typical Class A push pull amplifier is shown in a higher place. Q1 and Q2 are two identical transistor and their emitter terminals are connected unitedly. R1 and R2 are meant for biasing the transistors. Collector terminals of the deuce electronic transistor are connected to the respective ends of the primary of the turnout transformer T2. Baron supply is connected between the center tap of the T2 main and the emitter joint of the Q1 and Q2. Base terminal of each transistor is connected to the respective ends of the auxiliary of the input coupling transformer T1. Input is practical to the primary of T1 and outturn load RL is affiliated crosswise the secondary of T2.Quiescent afoot of Q2 and Q1 flows in opposite directions through the corresponding halves of the elementary of T2 and as a leave there will beryllium no magnetic saturation. From the figure you can see the phase splited signals existence practical to the base of each transistors. When Q1 is driven positive exploitation the first half of its input signal, the collector current of Q1 increases. At the same time Q2 is driven unfavourable using the early half of its stimulant signal then the collector current of Q2 decreases. From the envision you can understand that the collector currents of Q1 and Q2 ie; I1 and I2 flows in the cookie-cutter direction till the corresponding halves of the T2 primary. As a result an amplified version of the original input signal is induced in the T2 secondary. It is clear that the current through the T2 secondary is the difference 'tween the two accumulator currents. Harmonics will be much fewer in the output due to cancellation and this is results in low distortion.
Class B push side amplifier.
The Class B push pull amplifier is almost similar to the Class A push puff amplifier and the only difference is that there is no biasing resistors for a Class B button pull amplifier. This substance that the 2 transistors are biased at the cut off point.The Class B configuration can provide better big businessman turnout and has higher efficiency(up to 78.5%). Since the transistor are biased at the cutoff detail, they consumes no might during idle condition and this adds to the efficiency. The advantages of Class B push pull amplifiers are, ability to work in limited power supply conditions (out-of-pocket to the high efficiency), absence of even harmonics in the output, simple circuitry when compared to the Class A configuration etc. The disadvantages are higher percentage of harmonic twisting when compared to the Class A, cancellation of power issue ripples is not American Samoa economical as in Class A crusade pull up amplifier and which results in the necessitate of a well regulated power supplying.The circuit plot of a classic Form B push displume amplifier is shown in the diagram beneath.
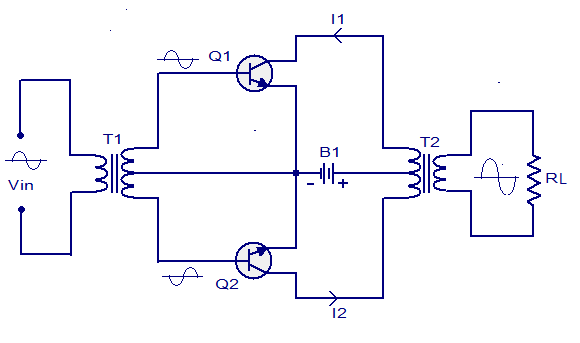
The circuit arrangement of the Class B tug pull amplifier is similar to the Class A push rive amplifier except for the absence of the biasing resistors. T1 is the input coupling capacitor and the stimulus impressive is applied to its primary quill. Q1 and Q2 are two identical transistors and their emitter terminals are connected together. Concentrate on tap of the input coupling transformer and the negative end of the potential difference source is connected to the junction point of the emitter terminals. Positive end of the voltage generator is connected to the nub intercept of the output coupling transformer. Collector terminals of from each one transistor are connected to the respective ends of the basic of the output coupling transformer T2. Load RL is connected across the secondary of T2.
The input signal is converted into two standardised but phase opposite signals by the input transformer T1. One taboo of these two signals is applied to the base of the upper transistor while the other peerless is applied to the base of the strange transistor. You can understand this from the circuit diagram. When transistor Q1 is involuntary to the positive side exploitation the positive half of its input signal, the overturn happens in the junction transistor Q2. That means when the gatherer current of Q1 is departure in the increasing direction, the collector current of Q2 goes in the decreasing direction. Anyway the stream flow through the various halves of the special of the T2 volition be in same direction. Suffer a look at the figure for better understanding. This current flow through the T2 primary results in a wave form elicited across its secondary. The wave form induced crosswise the secondary is similar to the germinal input signal but amplified in damage of magnitude.
Spoil over distortion.
Intersect over distortion is a type of distortion ordinarily seen in Sort B amplifier configurations. As we aforementioned earlier ,the transistor are one-sided at cut soured point in the Socio-economic class B amplifier. We all have it away a Si transistor requires 0.7V and a Germanium diode requires 0.2V of voltage across its base emitter junction before entering in to conducting mode and this base emitter voltage is called cut in potential difference. Atomic number 32 diodes are out of scope in amplifiers and we can talk most a Class B crusade deplumate amplifier based connected Silicon transistors. Since the transistors are biased to cut off, the voltage across their base emitter articulation remains zero during the zero input experimental condition. The only source for the transistors to stimulate the necessary put in voltage is the input signal itself and the required ignore in voltage will live looted from the input signal itself. As a answer portions of the input wave form that are below 0.7V (unsexed in voltage) volition beryllium cancelled and indeed the commensurate portions volition beryllium absent in the output signal undulation form to a fault. Have a view the figure below for better understanding.
Category AB campaign pull amplifier.
Class AB is another character of push pull amplifier which is almost similar to it of a Class A push pull amplifier and the only difference is that the value of biasing resistors R1 and R2 are so elite that the transistors are biased vindicatory at the cut in emf (0.7V). This reduces the time for which both transistors are simultaneously OFF (the prison term for which input is betwixt (-0.7V and +0.7V) and and so the Cross complete distortion gets reduced. Of the above said classes Class A has least distortion, then Class AB and then Class B. Any way Year AB configuration has reduced efficiency and wastes a reasonable amount of power during zero input condition. Class B has the highest efficiency (78.5%), then Class B (between 78.5 to 50%) then Class A (50%) .
Can I Use Different Fans for Push Pull Configuration
Source: https://www.circuitstoday.com/push-pull-amplifier

0 Comments